Question 1
Durée : 7 mn
Note maximale : 12
Question
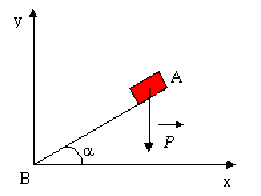
Une tuile faîtière de masse \(m\) glisse le long d'un toit incliné d'un angle \(\alpha\) sur l'horizontale.
Quel est le travail effectué par le poids de la tuile après le parcours \(AB\) ? Pour cela, utiliser la forme analytique du produit scalaire.
Application numérique : \(m = 5 \textrm{ kg}\) ; \(\alpha = 30^{\circ}\) ; \(AB = 6 \textrm{ m}\) ; \(g = \mathrm{9,81 m.s}^{-2}\)
Solution
Le travail du poids au cours de ce déplacement est \(W = \overrightarrow{P} \cdot \overrightarrow{AB}\)
Expressions des composantes de \(\overrightarrow{P}\) et \(\overrightarrow{AB}\):
\(\overrightarrow{P} =(0,-mg)\) et \(\overrightarrow{AB} = (-AB \cos 30^{\circ}, -AB \sin 30 ^{\circ})\)
d'où
\(\begin{array}{ll} W&=\overrightarrow{P} \cdot \overrightarrow{AB} \\&=(0,mg)\cdot(-AB \cos 30^{\circ}, -AB \sin 30^{\circ}) \end{array}\)
\(W = +mg ~AB \sin 30^{\circ}\) ( 4 points )
Application numérique :
\(W = 5 \times \mathrm{9,81} \times 6 \times \mathrm{0,5} = \textrm{147,15 J}\) ( 4 points )