Fonction tangente hyperbolique
Définition et propriétés
Définition :
La fonction tangente hyperbolique est définie sur \(\mathbb R\) par \(\textrm{th}x=\frac{\textrm{sh}x}{\textrm{ch}x}.\)
Propriété :
Autres formes \(\forall x \in \mathbb R~~\textrm{th}x=\frac{e^x-e^{-x}}{e^x+e^{-x}} = \frac{e^{2x}-1}{e^{2x}+1}=\frac{1-e^{-2x}}{1+e^{-2x}}.\)
La fonction th est impaire.
La fonction th est continue et dérivable, en appliquant la règle de dérivation d'un quotient,
on obtient \(\forall x \in \mathbb R~~(\textrm{th})'(x) = \frac{\textrm{ch}^2x-\textrm{sh}^2x}{\textrm{ch}^2x} = \frac{1}{\textrm{ch}^2x} = 1 -\textrm{th}^2x,\)
alors \(\forall x \in \mathbb R~~(\textrm{th})'(x)>0\)donc la fonction th est strictement croissante,
de plus \(\displaystyle \lim_{x\rightarrow+\infty}\textrm{th}x=1\)(C'est immédiat à partir de \(\forall x\in \mathbb R~~\textrm{th}x=\frac{1-e^{-2x}}{1+e^{-2x}}\) et \(\displaystyle \lim_{t\rightarrow-\infty}e^t = 0)\) et en utilisant l'imparité \(\displaystyle \lim_{x\rightarrow-\infty}\textrm{th}x=-1,\) enfin \(\textrm{th}0 = 0.\)
Variations et représentation graphique
Le tableau de variations suivant résume les propriétés de cette fonction :
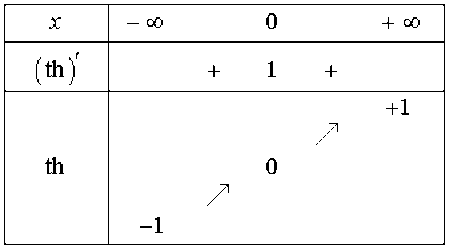
\(\color{blue} x \mapsto \textrm{th}x\)
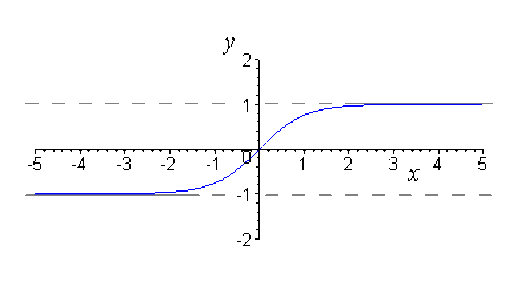
Par lecture du graphe, on retrouve que les droites d'équations \(y = -1, y = 1\)sont des asymptotes.
Le graphe est symétrique par rapport à l'origine.