Fonctions puissances
Théorème - définition
Définition : 1
Soit \(a\) un nombre réel strictement positif et \(b\) un réel quelconque. On définit le nombre réel \(a^b,\) appelé \(a\) puissance \(b,\) en posant : \(a^b = \exp(b\ln a).\)
Remarque : sur la cohérence avec la ressource
Fonctions \(x \mapsto x^n~~n \in \mathbb Z,~~x\mapsto \sqrt[n]{x}~~n\in\mathbb N^*,~~x\mapsto x^r~~r\in \mathbb Q.\)
Cette définition est cohérente car \(\forall n \in \mathbb N^*,\) \(\forall a>0\) \(\exp(n\ln a) = \exp(n\ln a))^n = a^n,\) on retrouve la puissance entière.
La définition précédente et les propriétés des fonctions logarithme et exponentielle permettent d'avoir les formules :
Si \(n\) est un entier strictement positif, \([\exp(\frac{1}{n}\ln a)]^n = \exp(n\frac{1}{n}\ln a) = \exp(\ln a) = a,\)
donc \(\exp(\frac{1}{n}\ln a) = a^{\tfrac{1}{n}} = \sqrt[n]{a}.\)
Si \(\frac{p}{q}\) est un élément de \(\mathbb Q,\) avec \(q > 0,\) \(\exp(\frac{p}{q}\ln a) = [\exp(\frac{1}{q}\ln a)]^p = (\sqrt[q]{a})^p\)
donc \(a^{\tfrac{p}{q}} = (\sqrt[q]{a})^p = (a^{\tfrac{1}{q}})^p.\)
Remarque :
Pour étudier une expression de la forme \(a^b\)avec \(b\) non entier, il est IMPERATIF de revenir à la définition \(a^b = \exp(b\ln a).\)
Définition : 2
Soit \(b\) un nombre réel quelconque, la fonction \(m :]0, +\infty[ \rightarrow \mathbb R\)définie par \(m(x) = x^b\) s'appelle une fonction puissance.
Ainsi \(\forall x >0~~m(x)=\exp(b\ln x)\)donc \(\ln m(x) = b\ln x,\) \(m\) est dérivable comme composée de fonctions dérivables et en utilisant la règle de dérivation des fonctions composées il vient
\(\forall x > 0~~m'(x) =\frac{b}{x}\exp(b\ln x) = b\exp(-\ln x)\exp(b\ln x) = b\exp((b-1)\ln x) = bx^{b-1}\)
d'où \(\boxed{\forall b \in \mathbb R~~\forall x>0~~\ln x^b = b\ln x,~~(x^b)'=bx^{b-1}}\)
Règles de calcul
\(\boxed{\forall (b,c) \in \mathbb R^2~~\forall x>0~~\forall y>0}\\\boxed{x^bx^c=x^{b+c}~~~~(1)} \boxed{x^by^b = (xy)^b~~~~(2)}\boxed{(x^b)^c=x^{bc}~~~~(3)}\\\boxed{\frac{x^b}{y^b} = (\frac{x}{y})^b~~~~(4)}\boxed{\frac{1}{x^b} = x^{-b}~~~~(5)}\boxed{}\)
Preuve : propriété (1)
On utilise les propriétés des fonctions exponentielle et logarithme,
\(x^bx^c=\exp(b\ln x)\exp(c\ln x) = \exp(b\ln x +c\ln x) = \exp((b+c)\ln x) = x^{b+c}\)
Preuve : propriété (2)
\(x^by^b = \exp(b\ln x)\exp(b\ln y) = \exp(b\ln x + b\ln y) = \exp[b(\ln x + \ln y)] = \exp(b\ln xy) = (xy)^b\)
Preuve : propriété (3)
\((x^b)^c = \exp(c\ln(x^b)) = \exp(cb\ln x) = \exp(bc\ln x) = x^{bc}\)
Propriété : propriété (4)
\(\frac{x^b}{y^b} = \frac{\exp(b\ln x)}{\exp(b\ln y)} = \exp(b\ln x - b\ln y) = \exp[b(\ln x-\ln y)] = \exp[b\ln(\frac{x}{y})] = (\frac{x}{y})^b\)
Preuve : propriété (5)
\(\frac{1}{x^b} = \frac{1}{\exp(b\ln x)} = \exp(-b\ln x) = x^{-b}\)
Variations et représentation graphique
En utilisant la valeur de la dérivée et les limites des fonctions logarithme et exponentielle, il vient :
\(\boxed{b <0~~\textrm{La fonction puissance est décroissante}}\\\boxed{\displaystyle \lim_{x\rightarrow 0}x^b = +\infty}\boxed{\displaystyle \lim_{x\rightarrow +\infty}x^b=0}\\ \\\boxed{b >0~~\textrm{La fonction puissance est croissante}}\\\boxed{\displaystyle \lim_{x\rightarrow 0}x^b = 0}\boxed{\displaystyle \lim_{x\rightarrow +\infty}x^b=+\infty}\\\boxed{0<b<1~~\displaystyle \lim_{x\rightarrow +\infty}\frac{x^b}{x} = 0}\boxed{b>1~~\displaystyle \lim_{x\rightarrow +\infty}\frac{x^b}{x}=+\infty}\)
\(\color{blue} x \mapsto x^{\pi}\)
\(\color{green} x \mapsto x^{0.8}\)
\(\color{cyan}x \mapsto x^{-2}\)
\(\color{red} x \mapsto x^0\)
\(\color{magenta} x \mapsto x^1\)
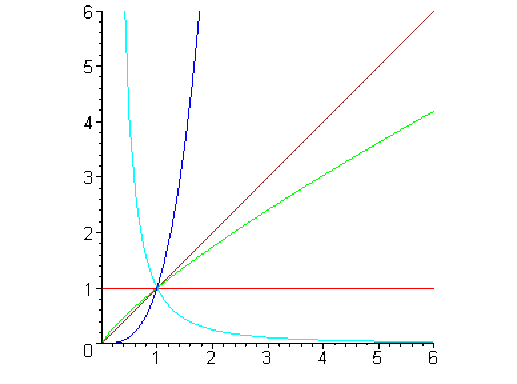
On observe que l'allure du graphe dépend des valeurs de \(b\):
\(b < 0\): Les droites \(x = 0\)et\(y = 0\) sont des asymptotes,
\(b >0\): Le graphe présente une branche parabolique...
\(0 <b < 1\): ... de direction horizontale \(\displaystyle \lim_{x\rightarrow +\infty}{\frac{x^b}{x}} = 0,\)
\(b > 1 \): ... de direction verticale \(\displaystyle \lim_{x\rightarrow +\infty} \frac{x^b}{x} = +\infty.\)