Question 2
Durée : 5 mn
Note maximale : 4
Question
Calculer l'intensité en \(P\), que mesure un récepteur de rayonnement si celle-ci s'exprime par : \(\underline{I} = \underline{G}_{m} \cdot \underline{G}^{\ast}_{m}\) (à une constante multiplicative près).
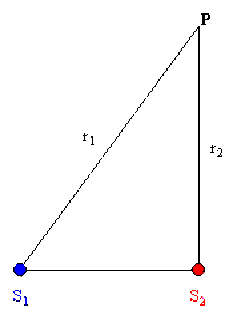
Solution
L'intensité s'exprime par :
\(\underline{I} = \underline{G}_{m} \cdot \underline{G}^{\ast}_{m} = \left(a_{1} e^{j \theta_{1}} + a_{2} e^{j \theta_{2}} \right) \left(a_{1} e^{-j \theta_{1}} + a_{2} e^{-j \theta_{2}} \right) = a_{1}^{2} + a_{2}^{2} + 2 a_{1} a_{2} \cos \left(\theta_{1} - \theta_{2} \right)\)
\(I = \frac{A_{1}^{2}}{r_{1}^{2}} + \frac{A_{2}^{2}}{r_{2}^{2}} + 2 \frac{A_{1} A_{2}}{r_{1} r_{2}} \cos \left[\frac{\omega}{v}\left(r_{2} - r_{1}\right) + \varphi_{1} - \varphi_{2}\right]\) ( 4 points )