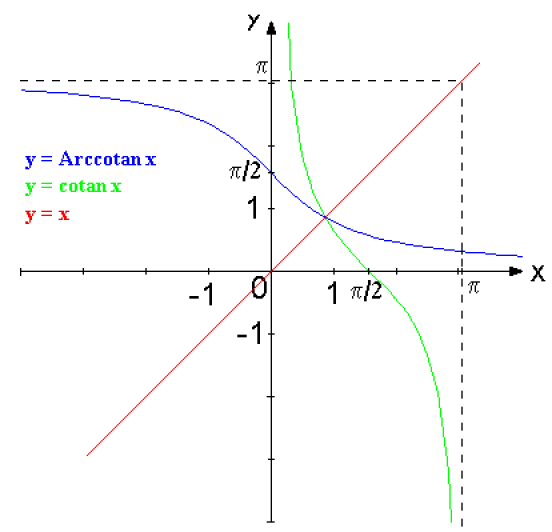
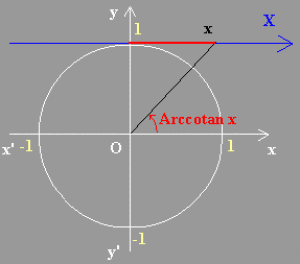
Fonction Arccotangente de x : Arccotan x
Définition :
L'application \(\tan\) : \(]0 ,~ \pi[ \to \mathbb{R}\) continue et strictement décroissante admet une fonction réciproque notée \(\textrm{cotan}^{-1}\) ou \(\textrm{Arccotan}\) : \(\mathbb{R} \to ]0 , \pi[\)
\(\begin{array}{llll} \sin (\textrm{Arccotan }x) = \frac{1}{\sqrt{1+x^{2}}} & \forall x \in\mathbb{R} \\ \textrm{cotan }(\textrm{Arccotan }x) = \frac{x}{\sqrt{1+x^{2}}}& \forall x \in\mathbb{R}\\\tan (\textrm{Arccotan }x) = \frac{1}{x} & \forall x \in\mathbb{R}^{\ast}\\\textrm{cotan }(\textrm{Arccotan }x) = x & \forall x \in\mathbb{R} \end{array}\)
fonction ni paire, ni impaire.
fonction dérivable sur \(\mathbb{R}\) et :
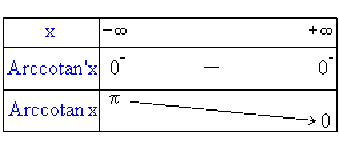
\(\textrm{Arccotan }' x = \frac{1}{\textrm{cotan}'(\textrm{Arccotan }x)} = \frac{1}{-\left[1+\textrm{cotan}^{2}(\textrm{Arccotan }x)\right]} = -\frac{1}{1+x^{2}}<0\)
donc fonction décroissante sur \(\mathbb{R}\).
tableau de variation :
Représentation graphique de Arccotan x