Fonction tangente hyperbolique de x : th x
La fonction tangente hyperbolique, notée \(\textrm{th}\) , est :
définie sur \(\mathbb{R}\) :
\(\textrm{th}x = \frac{\textrm{sh}x}{\textrm{ch}x} = \frac{e^{x} - e^{-x}}{e^{x} + e^{-x}} = \frac{e^{2x} - 1}{e^{2x} + 1} = \frac{1-e^{-2x}}{1+ e^{-2x}}\)
impaire :
\(\textrm{th} (-x) = \frac{\textrm{sh}(-x)}{\textrm{ch} (-x)} = - \frac{\textrm{sh}x}{\textrm{ch}x} = - \textrm{th}x\)
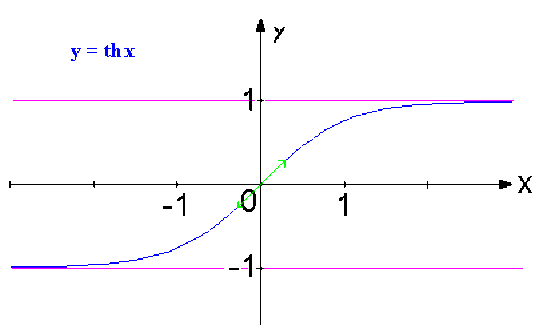
Le domaine d'étude se réduit à \(D_{e} = [0, +\infty [\) . Le graphe de la fonction tangente hyperbolique, admet l'origine \(O\) comme centre de symétrie.
Aux bornes de \(D_{e}\), nous avons :
\(\textrm{th }0 = \textrm{sh }0 / \textrm{ch }0 = 0\)
\(\displaystyle{\lim_{x \to + \infty} \textrm{th}x \approx \lim_{x \to +\infty} \frac{e^{2x}}{e^{2x}} = 1}\)
la droite d'équation \(y = 1\) est une asymptote horizontale.
La fonction dérivée \(\textrm{th'} x = (\textrm{sh }x / \textrm{ch }x )' = (\textrm{ch}^{2}x - \textrm{sh}^{2}x) / \textrm{ch}^{2}x = 1 - \textrm{th}^{2}x = 1 / \textrm{ch}^{2}x\) étant positive sur \(\textrm{D}_{e}\), la fonction \(\textrm{th }x\) est croissante sur \(\textrm{De}\) .
Tableau de variation sur \(D_{e}\)

Représentation graphique de \(\textrm{th }x\)